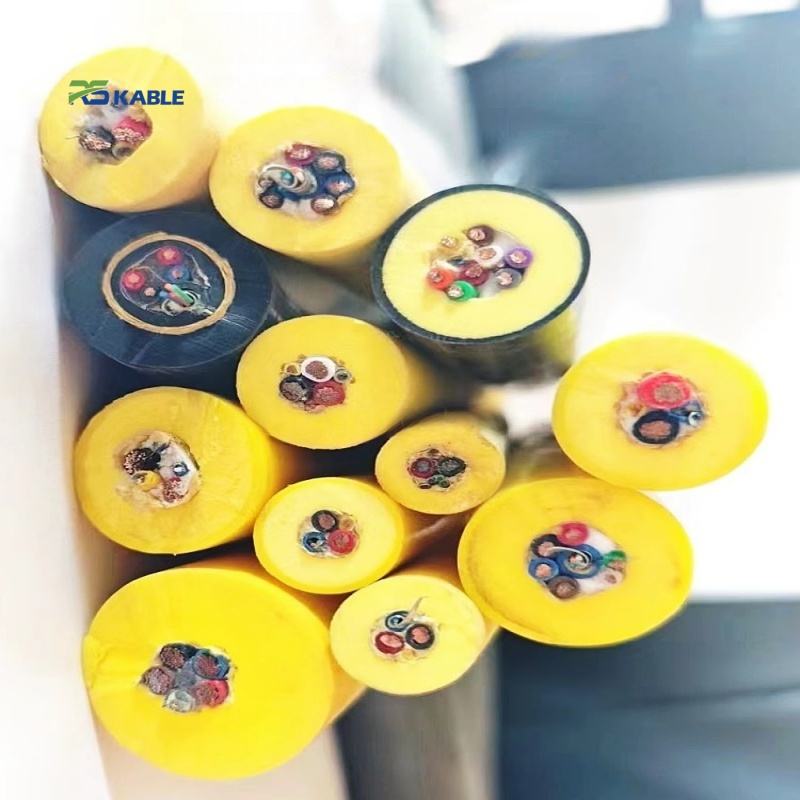
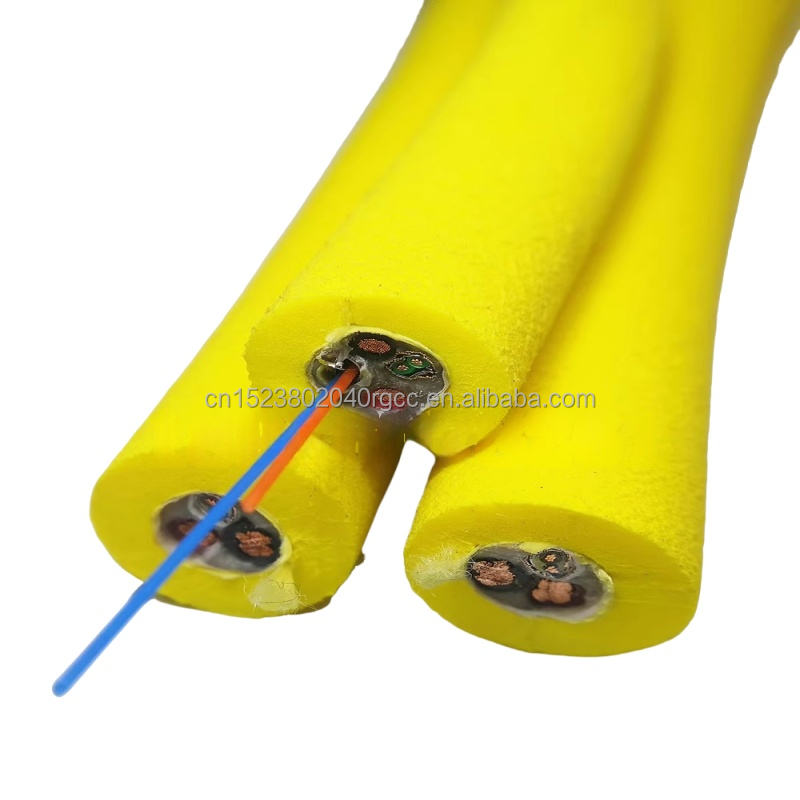
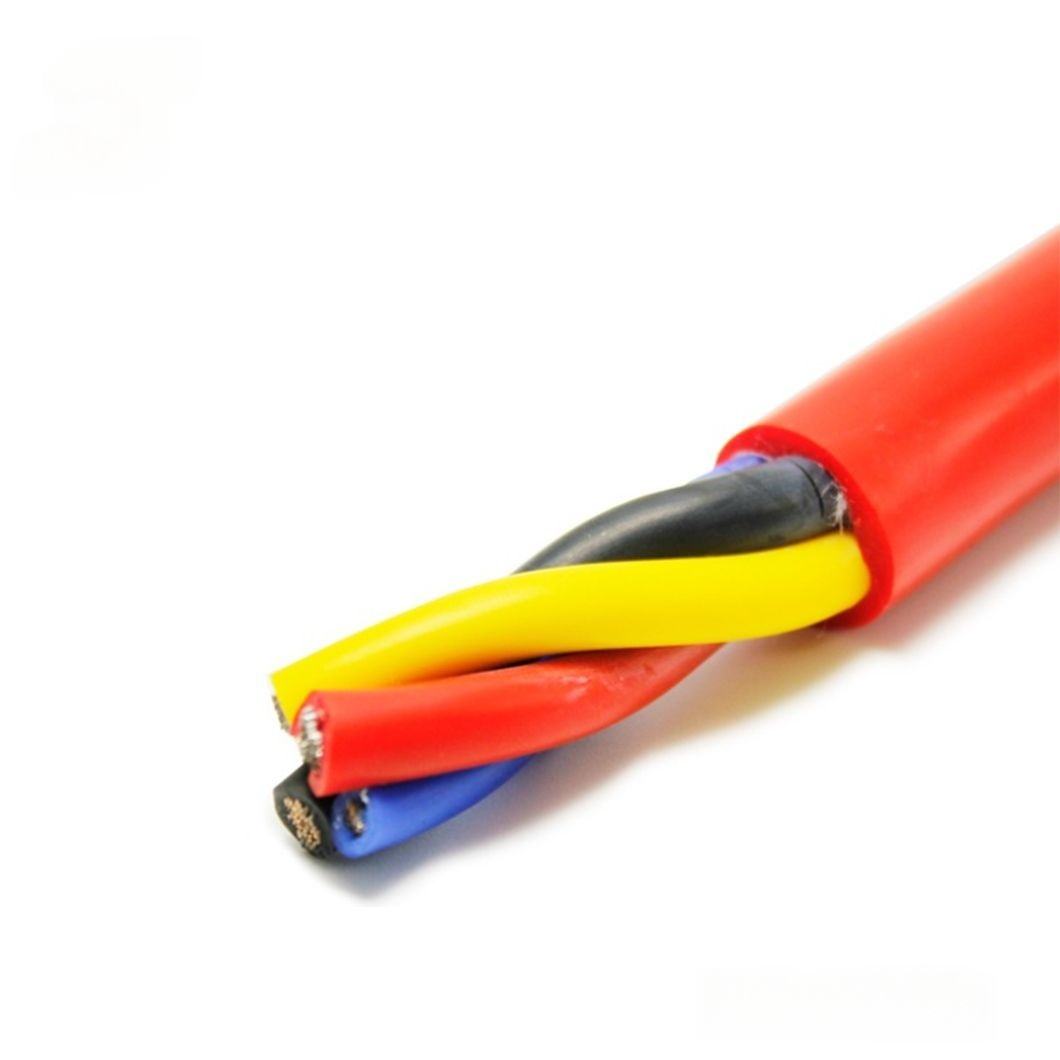
A Comprehensive Guide to Subsea Data, Power, and Control Applications
Underwater cables—also known as submarine cables or subsea cables—are one of the most critical yet least visible infrastructures supporting the modern world. Hidden beneath oceans, seas, rivers, and lakes, these specialized cables enable global internet connectivity, power offshore energy systems, support scientific discovery, and make deep-sea operations possible.
While many people associate underwater cables solely with international internet traffic, their real-world applications extend far beyond telecommunications. From underwater data cables and fiber optic submarine cables to ROV umbilicals and subsea power cables, each type serves a distinct and mission-critical purpose.
As global demand for data, renewable energy, and offshore exploration continues to rise, underwater cables have become a cornerstone of modern industry and digital infrastructure.
In this in-depth guide, we’ll explore what underwater cables are used for, how they function across industries, real-world examples, and why their importance will only grow in the coming decade.
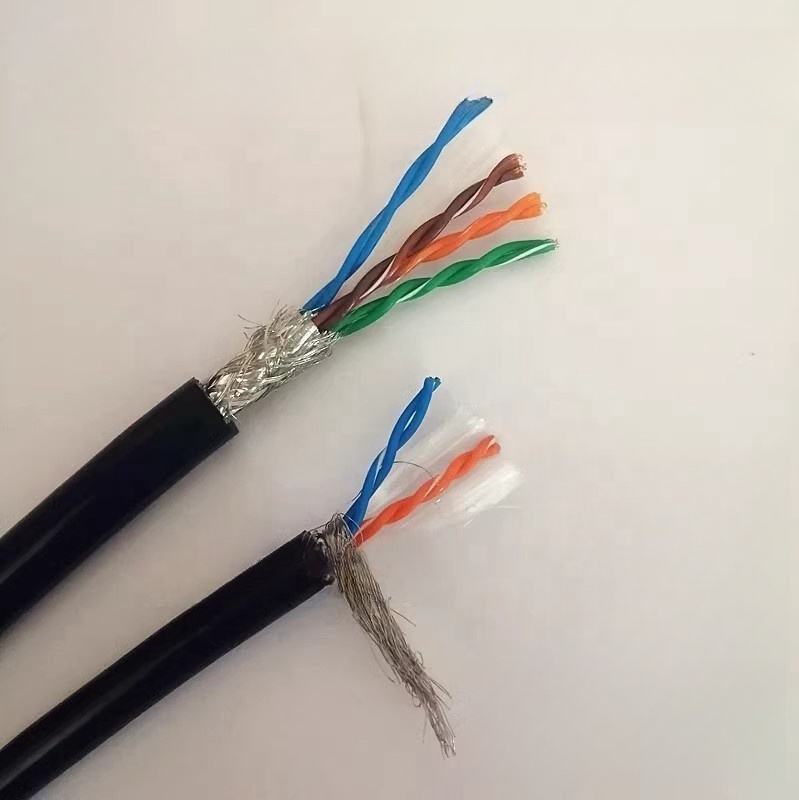

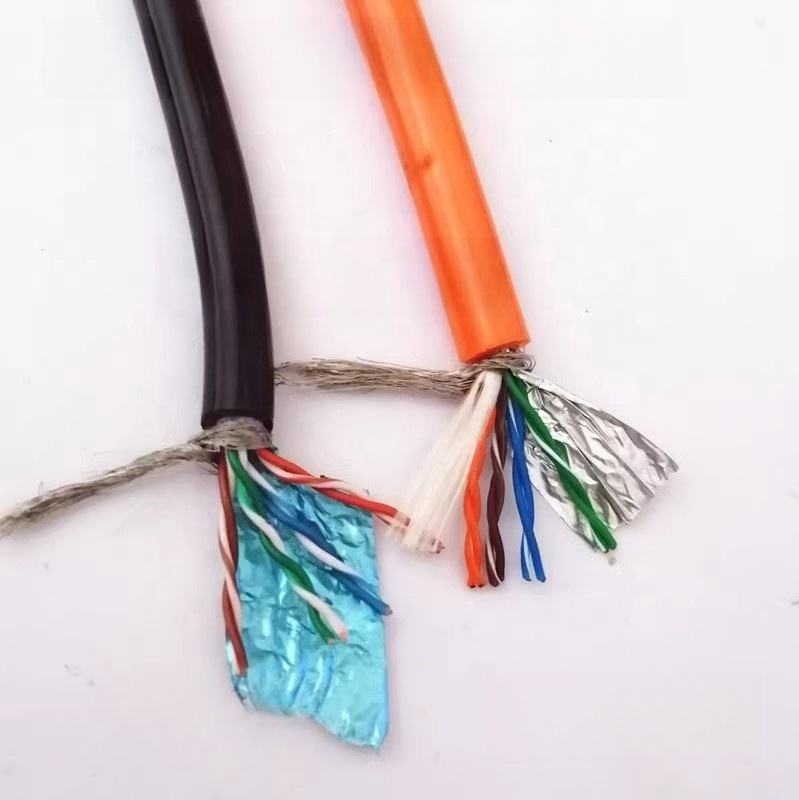
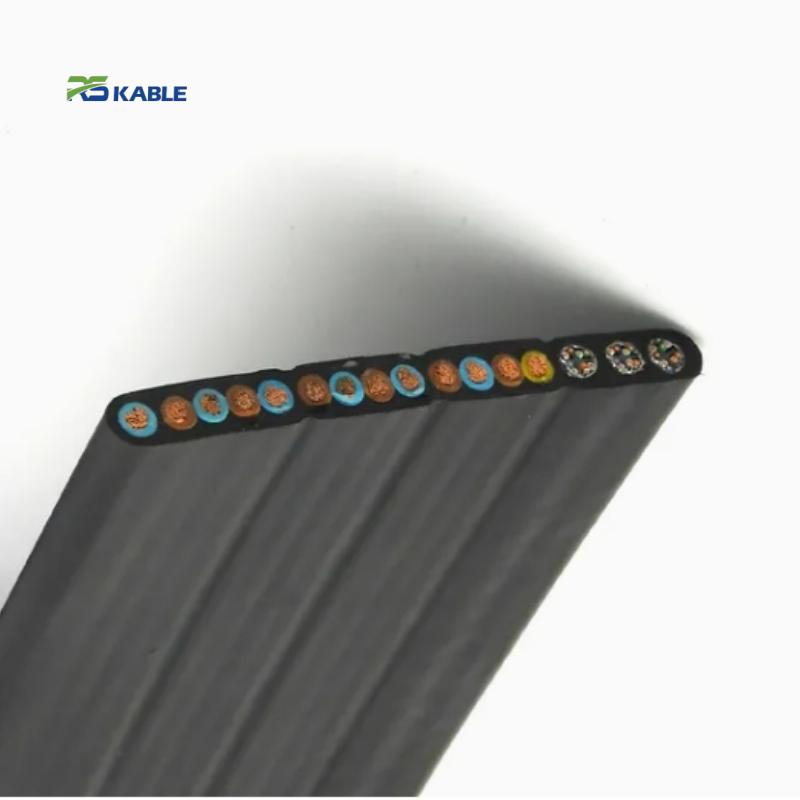
High Quality 4-Core Twisted Pair Drag Chain Cable | Corrosion-Resistant, Foldable Polyurethane Insulation with Polyethylene Conductor
High-quality flexible drag chain cable with 4 twisted pair cores for reliable power and signal transmission under continuous motion. Polyurethane insulation improves abrasion and corrosion resistance while polyethylene conductors ensure excellent conductivity. Ideal for automated machinery, robotics, and industrial cable chain systems. :contentReference
What Are Underwater Cables?
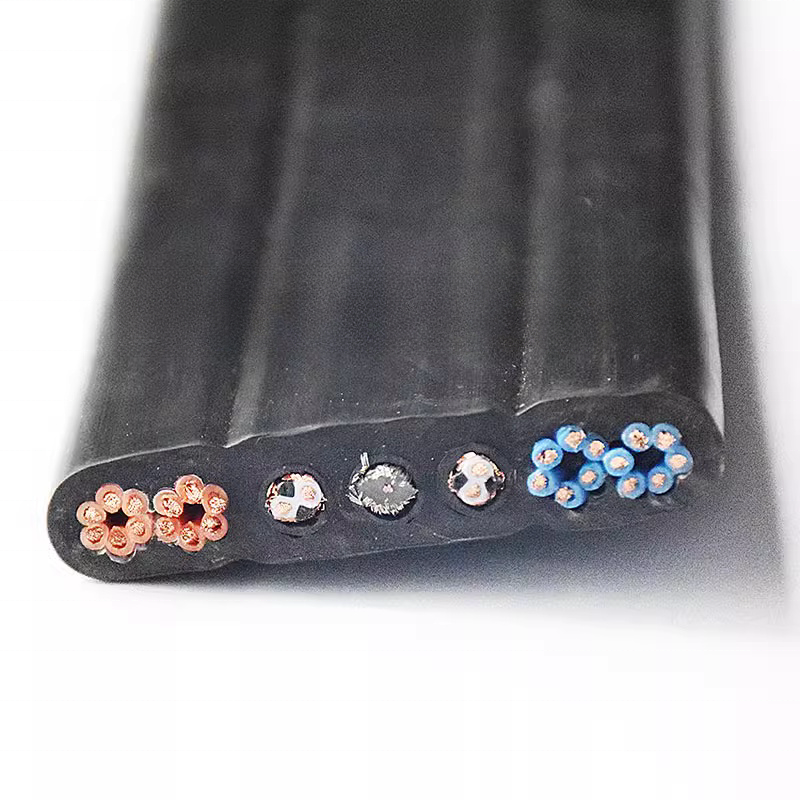
Underwater cables are specially engineered cables designed to operate reliably in submerged environments—often under extreme pressure, corrosion, mechanical stress, and long-term exposure to seawater.
Depending on their application, underwater cables may transmit:
-
High-speed data and communications
-
Electrical power
-
Control and monitoring signals
-
Or a combination of power + data + strength members
Common categories include:
-
Submarine fiber optic cables
-
Underwater data cables
-
Subsea power cables
-
ROV and AUV umbilical cables
-
Scientific and sensing cables
Each plays a different role in global infrastructure.
Primary Use: Global Internet and Data Transmission
The Backbone of the Global Internet
The most widely known use of underwater cables is international telecommunications. Over 99% of intercontinental internet traffic is carried by submarine fiber optic cables, not satellites.
These underwater data cables connect continents and countries, enabling:
-
Cloud computing
-
Video streaming
-
Financial transactions
-
AI data transfer
-
International communications
Modern fiber optic underwater cables can transmit terabits per second using advanced optical amplification and wavelength-division multiplexing (WDM).
Without them, global digital services would experience massive latency, instability, or complete failure.
Underwater Data Cables Beyond the Open Ocean
Underwater data cables are not limited to transoceanic routes. They are also widely used in:
-
Coastal communication networks
-
Island-to-mainland connectivity
-
Offshore platforms
-
Subsea monitoring systems
-
Smart ports and underwater sensor networks
These systems often use ruggedized fiber optic cables designed for shallow water, near-shore environments, and inland water bodies.
As edge computing and IoT expand offshore, demand for localized underwater data cables continues to grow.
Offshore Energy: Powering Oil, Gas, and Renewables
Oil & Gas Operations
In offshore oil and gas fields, underwater cables are essential for:
-
Powering subsea pumps and compressors
-
Transmitting sensor data
-
Controlling valves and production equipment
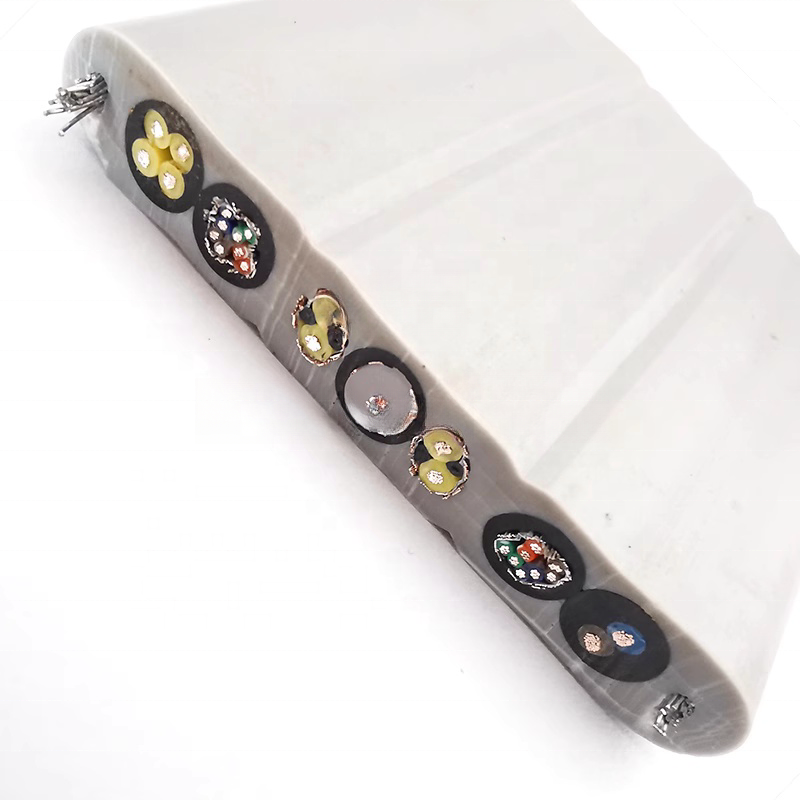
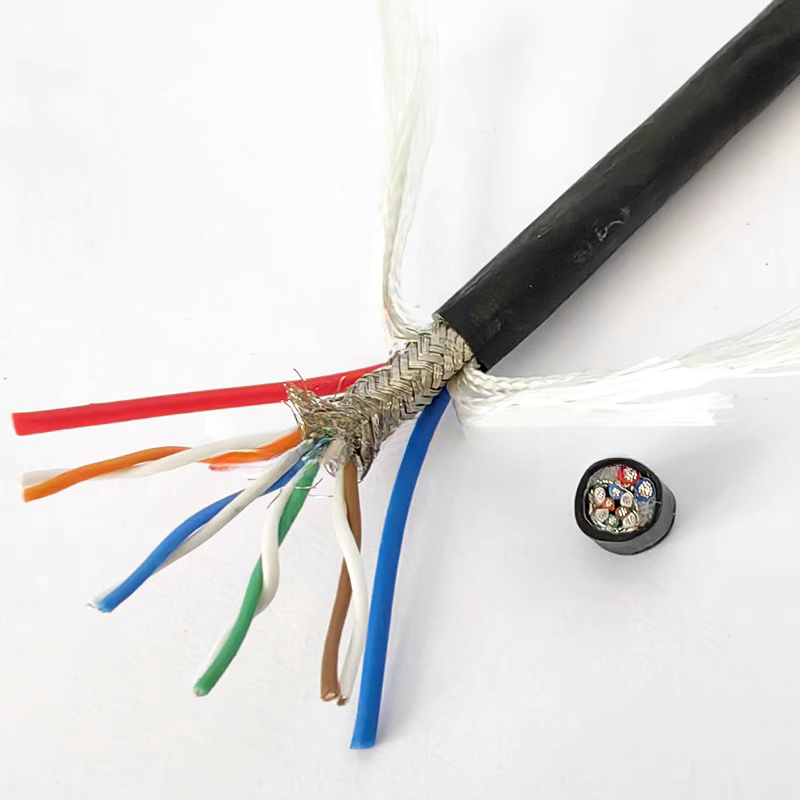
These systems often rely on electro-hydraulic or electro-optical umbilical cables, combining power conductors, fiber optics, and fluid lines in a single composite structure.
Such cables must operate reliably at depths exceeding 3,000 meters, under high pressure and constant mechanical stress.
Offshore Wind and Renewable Energy
Underwater power cables are also critical to the global energy transition.
They are used to:
-
Export electricity from offshore wind farms
-
Connect subsea substations
-
Transmit high-voltage power to onshore grids
High-Voltage AC (HVAC) and HVDC submarine cables enable efficient long-distance power transmission with minimal losses.
As offshore wind capacity expands globally, subsea power cable deployment continues to accelerate.
ROVs and Underwater Robotics
The Lifeline of Deep-Sea Operations
Remotely Operated Vehicles (ROVs) and Autonomous Underwater Vehicles (AUVs) depend on specialized underwater cables—commonly known as umbilical cables or tethers.
These cables typically integrate:
-
Copper conductors for power
-
Fiber optics for real-time video and data
-
Aramid or steel strength members for tensile load
-
Neutral buoyancy materials for stability
ROV cables are used in:
-
Offshore inspection and maintenance
-
Pipeline surveys
-
Subsea construction
-
Scientific exploration
-
Search and recovery operations
Without these cables, precise real-time control and high-definition data transmission in deep water would be impossible.
Scientific Research and Ocean Observation
Enabling Real-Time Ocean Science
Underwater cables play a key role in advancing marine science and climate research.
Subsea observatory networks use powered underwater cables to connect:
-
Seismic sensors
-
Temperature and pressure instruments
-
Chemical and biological monitoring systems
These cables supply continuous power and allow real-time data transmission from the seafloor to onshore research centers.
In recent years, existing submarine fiber optic cables have even been repurposed for distributed acoustic sensing (DAS)—transforming communication cables into massive seismic and environmental monitoring arrays.
Military and Defense Applications
Underwater cables also hold strategic importance in national defense.
They are used for:
-
Secure military communications
-
Sonar and surveillance networks
-
Submarine detection systems
-
Naval base connectivity
Because of their importance, subsea cable security and redundancy have become growing concerns in geopolitics and defense planning.
Emerging Applications of Underwater Cables
As technology evolves, underwater cables are finding new and innovative uses:
-
AI and hyperscale data centers requiring ultra-low latency connections
-
Environmental monitoring using sensor-embedded cables
-
Smart aquaculture and fisheries management
-
Deep-sea mining and exploration
-
Arctic and polar connectivity routes enabled by changing sea ice conditions
These emerging applications continue to expand the role of underwater cable systems well beyond traditional telecom use.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite their importance, underwater cable systems face several challenges:
-
High installation and maintenance costs
-
Environmental protection requirements
-
Risks from fishing activities, anchors, and seismic events
-
Long-term durability in corrosive environments
Modern cable design focuses on enhanced armoring, redundancy, and environmentally responsible installation practices to mitigate these risks.
Why Underwater Cables Matter More Than Ever
So, what are underwater cables used for?
They are used for far more than internet connectivity.
Underwater cables:
-
Carry the world’s data
-
Power offshore energy systems
-
Enable deep-sea robotics
-
Advance scientific discovery
-
Support national security
From global fiber optic networks to specialized ROV umbilicals, underwater cables form the unseen foundation of our connected and industrialized world.
As demand for data, energy, and ocean exploration continues to grow, underwater cables will remain a critical technology shaping the future beneath the surface.
FAQ: Underwater Cables
What is the main purpose of underwater cables?
Primarily to transmit global internet data, but they are also used for power delivery, control systems, and scientific monitoring.
Do underwater cables only transmit data?
No. Many underwater cables transmit electrical power or combine power, data, and mechanical support in one system.
Are underwater cables used in renewable energy?
Yes. Offshore wind farms rely heavily on subsea power cables to transmit electricity to shore.
How long do underwater cables last?
Well-designed submarine cables can operate for 25–40 years with proper protection and maintenance.
What industries rely most on underwater cables?
Telecommunications, offshore energy, marine research, defense, and underwater robotics.