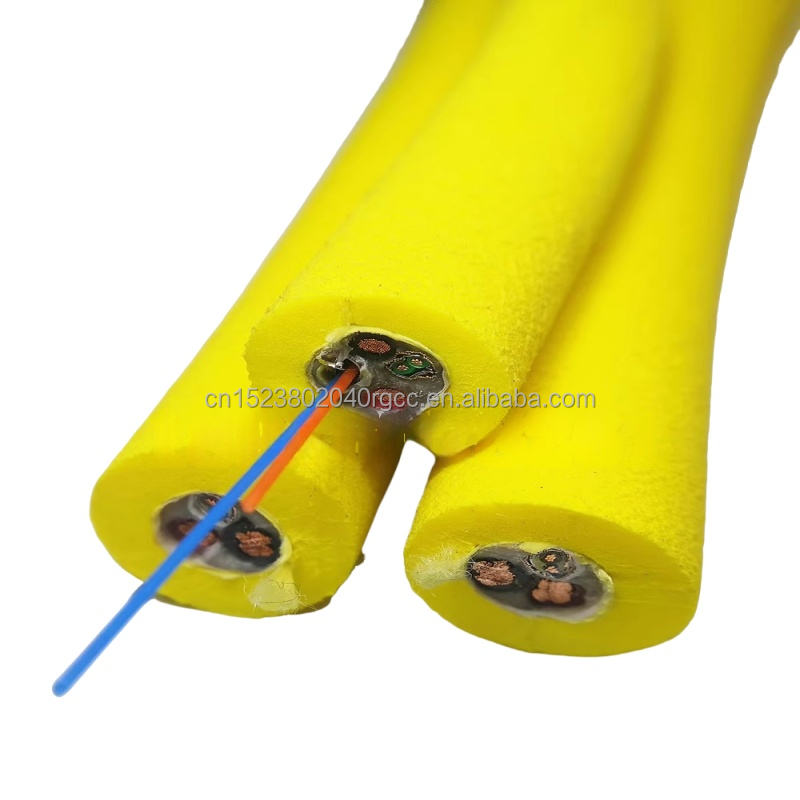
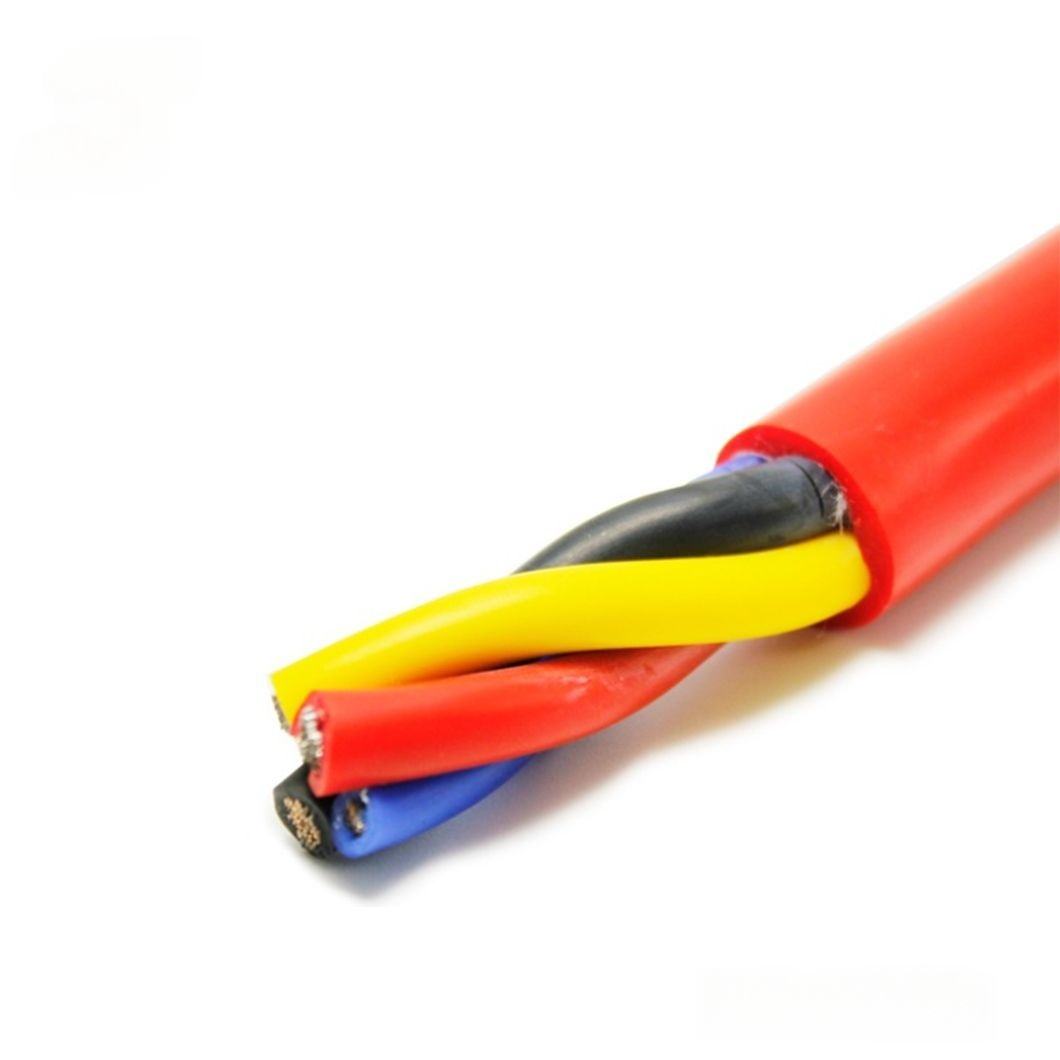
Industrial Cable: Understanding Types, Applications, and Solutions
In industrial environments, reliability is rarely optional. Power interruptions, signal loss, or premature component failure can halt production lines, compromise safety, and drive up operating costs. At the center of this reliability chain lies a component that often receives little attention until something goes wrong: the industrial cable.
An industrial cable is not simply a conductor wrapped in insulation. It is a purpose-built system designed to perform consistently under mechanical stress, electrical load, and environmental exposure that far exceed normal commercial conditions. From automated factories and energy facilities to ports, mines, and offshore platforms, these cables form the physical link between power, control, and modern industrial intelligence.
This article takes a practical, experience-driven look at industrial cables—what defines them, how different types are used, where failures typically occur, and how to select solutions that support long-term performance rather than short-term savings.
What Makes an Industrial Cable Different?
The defining feature of an industrial cable is not its voltage rating alone, but its ability to operate continuously in demanding conditions. While residential or commercial cables are designed for static installation, industrial cables must often endure:
-
Constant vibration or repeated flexing
-
Exposure to oils, chemicals, moisture, or UV radiation
-
Temperature extremes and thermal cycling
-
Electromagnetic interference from motors and drives
-
Mechanical loads such as tension, torsion, or abrasion
To meet these demands, an industrial cable is engineered as an integrated structure—conductor design, insulation system, shielding, and outer jacket are selected together to match a specific duty profile.
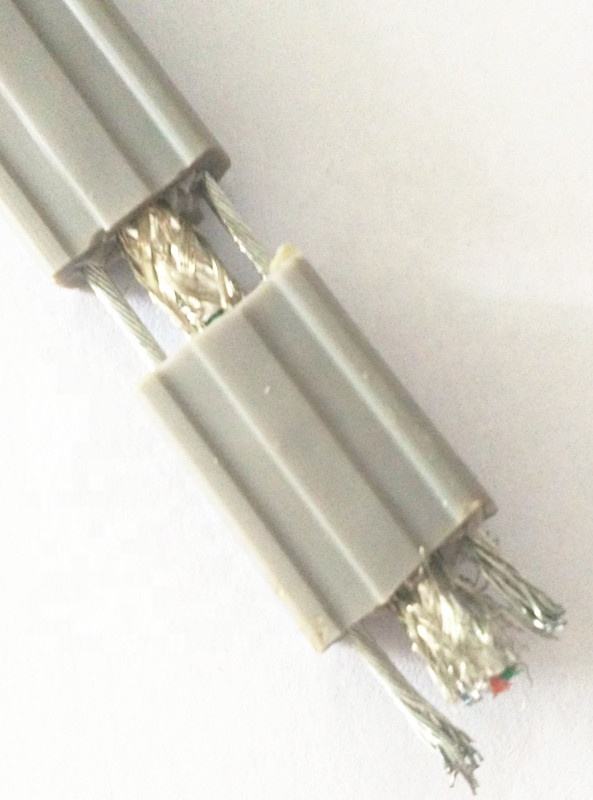

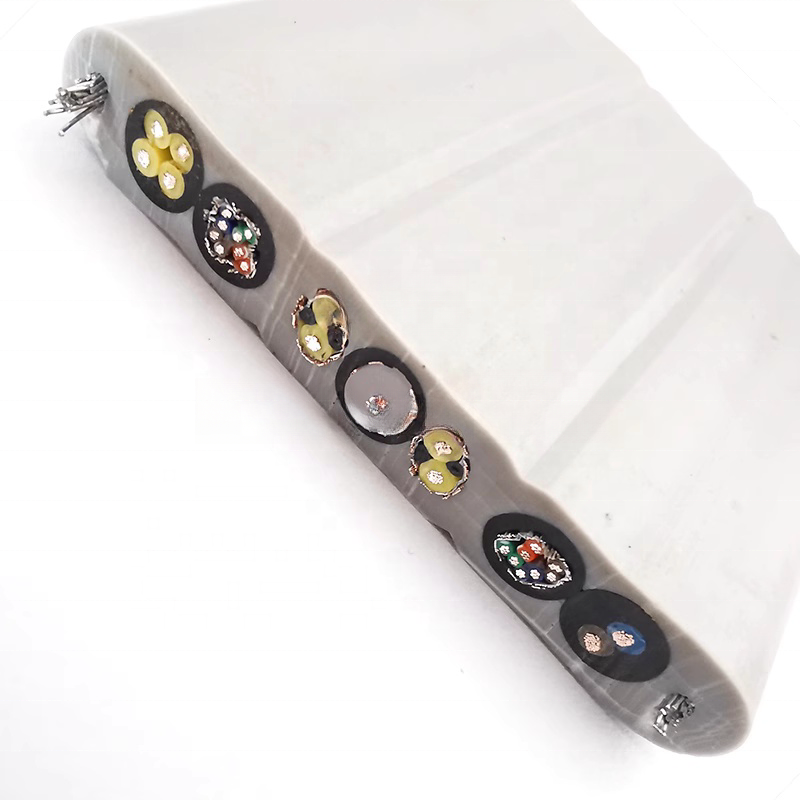
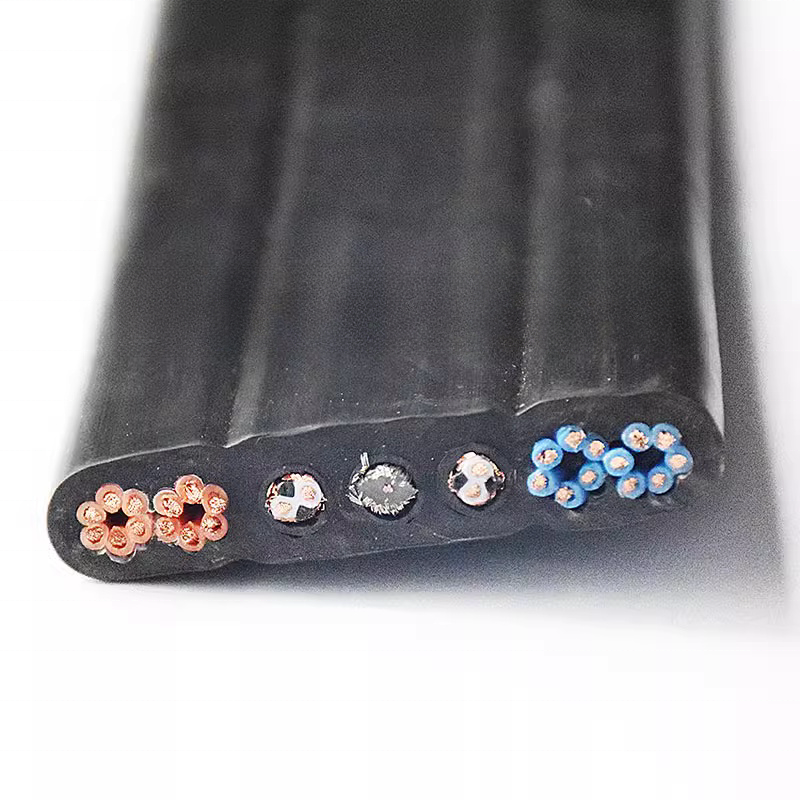
Cold‑Resistant Flat CCTV Elevator Cable – Dual‑Steel Reinforced, Dual‑Shielded Cat5e/6A, PE Insulated
A flexible flat CCTV/elevator cable engineered for cold environments, featuring dual‑steel reinforcement for high tensile strength and dual shielding for superior interference resistance. PE insulation ensures reliable performance for Cat5e and Cat6A signal transmission in elevator monitoring and network applications.
- Cold‑resistant flat profile for elevator CCTV and network cable applications
- Dual steel reinforcement for mechanical strength and durability
- Dual shielding to block electromagnetic interference for stable data transmission
- Supports Cat5e and Cat6A network performance standards
- PE insulation for enhanced environmental resistance
Core Categories of Industrial Cables
Rather than being defined by appearance, industrial cables are classified by function and operating conditions.
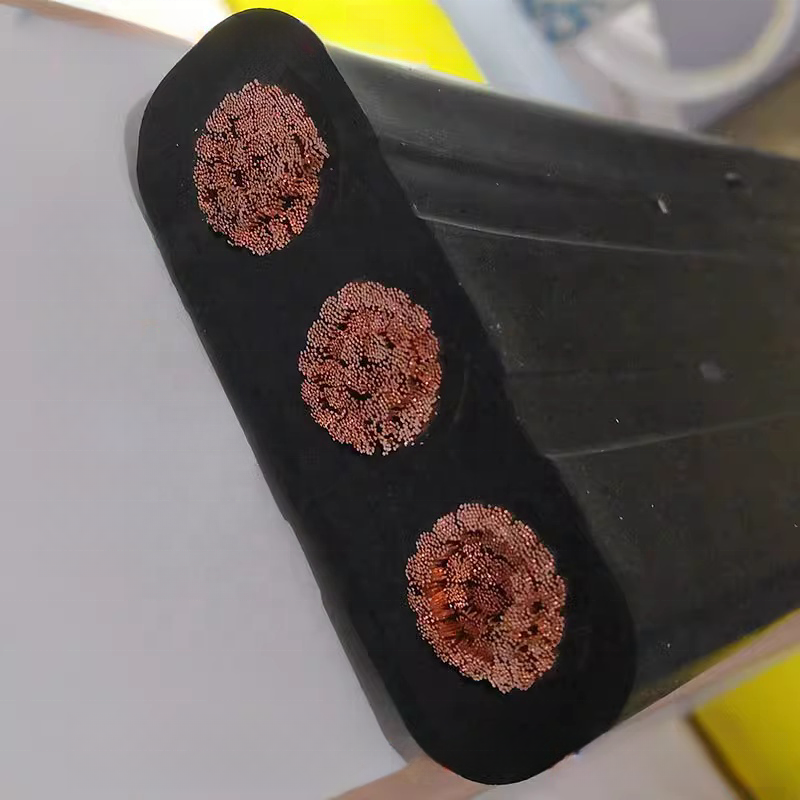
Power Cables
Power cables deliver electrical energy to motors, drives, and equipment. In industrial settings, they typically feature thicker insulation, higher temperature ratings, and optional armoring for mechanical protection.
Common applications include:
-
Motors and pumps
-
Power distribution systems
-
Heavy machinery
Material selection is driven by current load, heat dissipation, and environmental exposure.
Control Cables
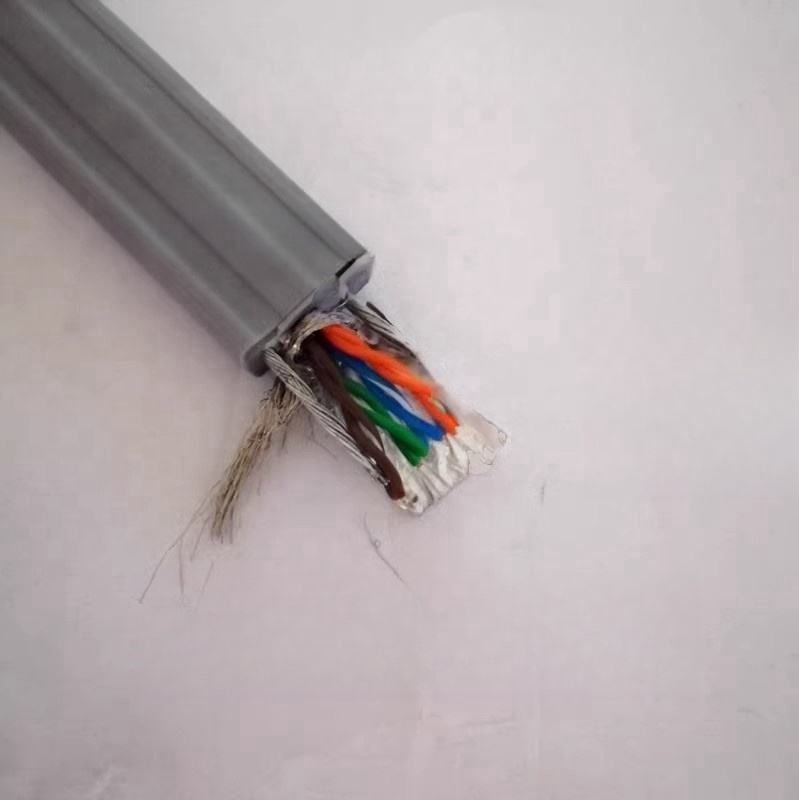
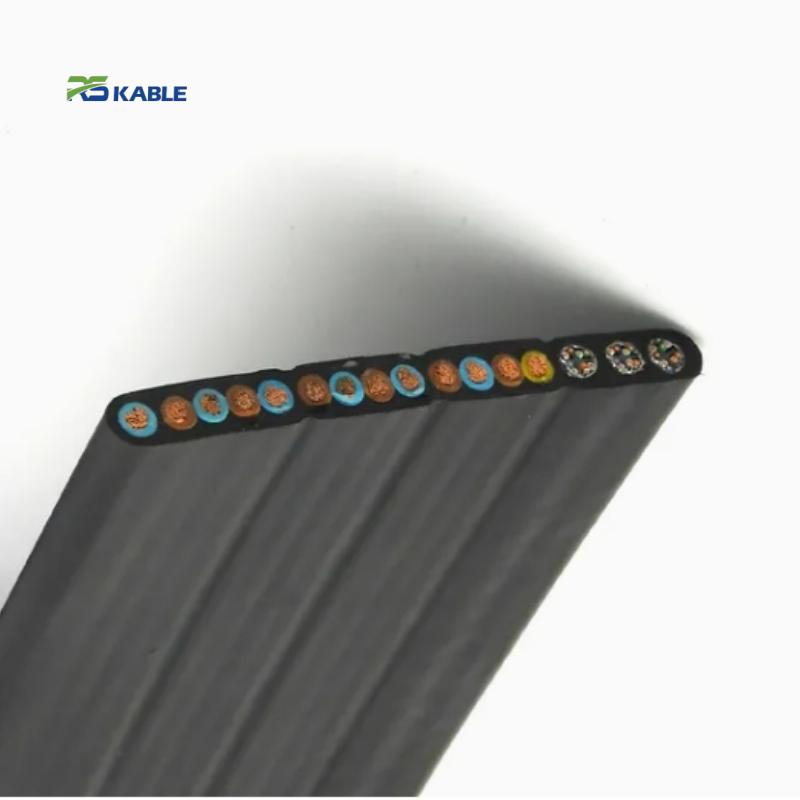
Control cables transmit low-voltage signals that govern machine operation. These multi-core cables are essential for automation, PLC systems, and interlocking controls.
Shielded versions are widely used to prevent signal distortion in electrically noisy environments.
Flexible and Continuous-Flex Cables
In dynamic applications—robotics, drag chains, moving gantries—standard cables fail quickly. Flexible industrial cables use fine-stranded conductors and optimized lay lengths to survive millions of bending cycles.
Here, mechanical endurance is as important as electrical performance.
Instrumentation and Signal Cables
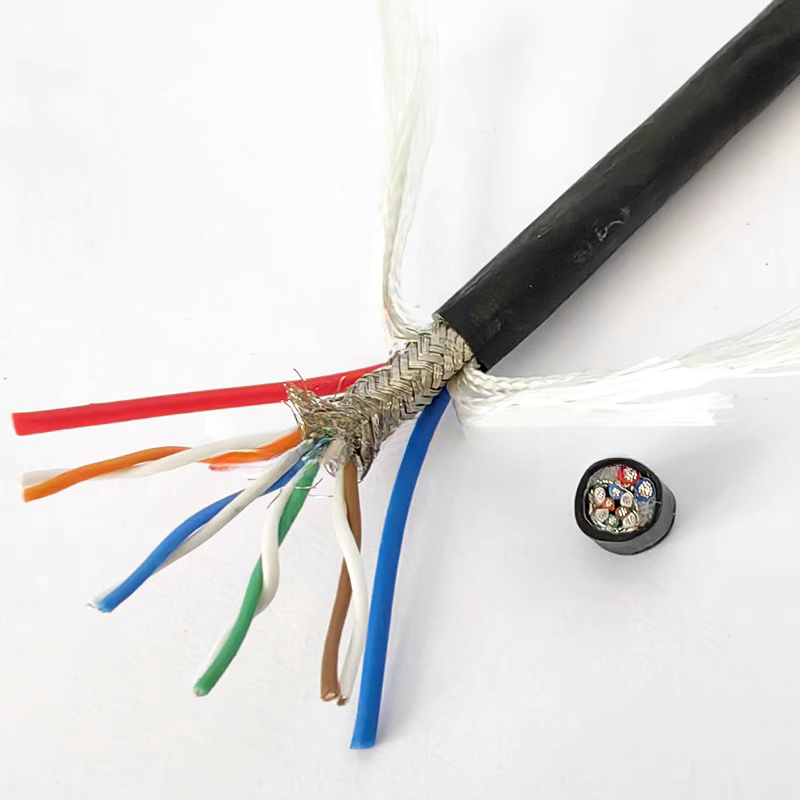
Instrumentation cables carry low-level signals from sensors and measurement devices. Accuracy and noise resistance are critical, making pair twisting and shielding essential design features.
These cables are common in:
-
Process control systems
-
Power plants
-
Oil and gas facilities
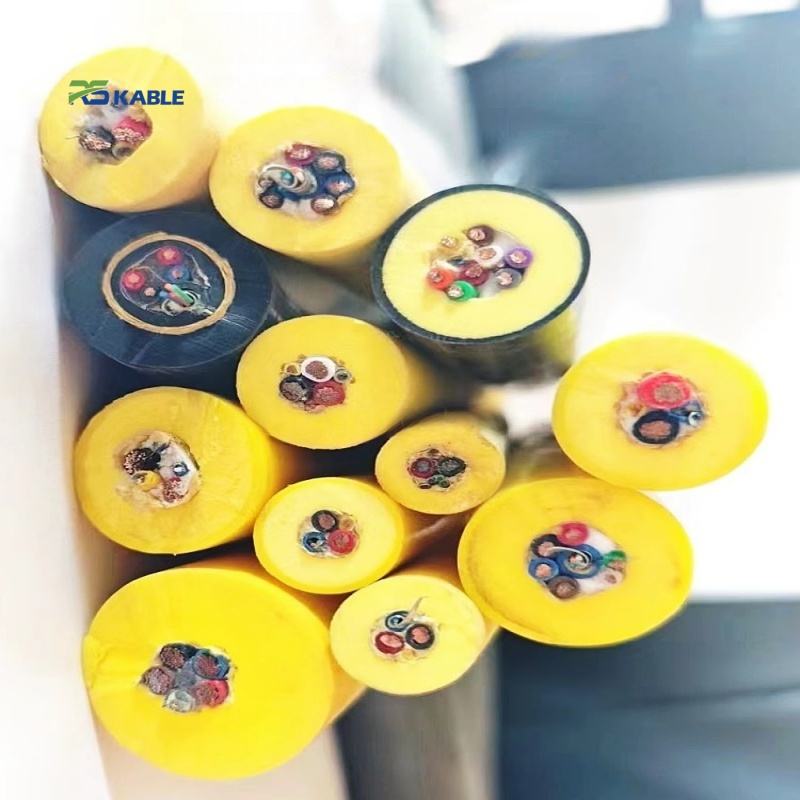
Specialty Industrial Cables
Some environments demand highly specialized designs, such as:
-
Elevator traveling cables
-
Crane and hoisting cables
-
Subsea and marine cables
-
High-temperature furnace cables
In these cases, the industrial cable is often custom-engineered to meet project-specific mechanical and environmental requirements.
Design Features That Determine Reliability
The long-term performance of an industrial cable depends on details that are not always visible from the outside.
Conductor Construction
Fine-stranded copper conductors improve flexibility and fatigue resistance. Stationary installations may tolerate fewer strands, while dynamic systems demand higher strand counts.
Insulation and Jacket Materials
Material choice affects resistance to oil, chemicals, abrasion, heat, and flame propagation. Common options include PVC, TPE, PUR, rubber, and halogen-free compounds—each with trade-offs.
Shielding and EMI Protection
In environments with variable-frequency drives or high-power motors, shielding prevents electromagnetic interference that can disrupt control and data signals.
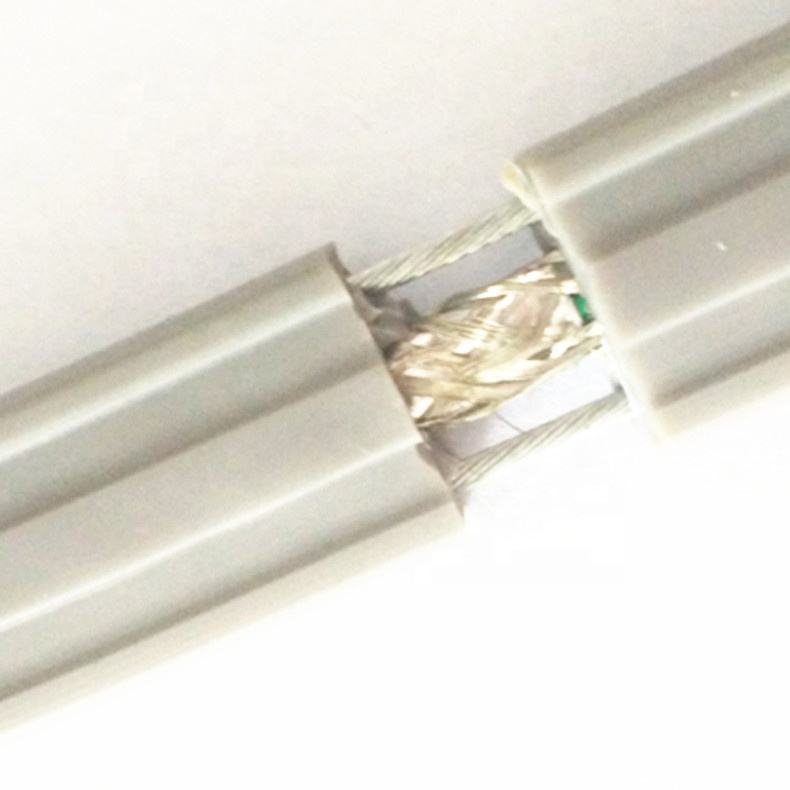
Mechanical Reinforcement
Long vertical runs or moving applications may require steel wires or aramid fibers to manage tensile loads without overstressing conductors.
These elements work together to ensure the Industrial Cable performs reliably over its intended service life.
Where Industrial Cables Are Used in Practice
Industrial cables are present wherever operational continuity and safety matter.
Manufacturing and Automation
Production lines rely on control and flexible cables to connect machines, sensors, and controllers. Cable failure here often means immediate downtime.
Energy and Utilities
Power generation and distribution systems use cables designed for thermal stability, outdoor exposure, and long service life.
Ports, Cranes, and Material Handling
Moving equipment demands cables that tolerate bending, tension, and environmental stress simultaneously.
Transportation and Infrastructure
Rail systems, elevators, and tunnels depend on specialized cables that meet strict safety and fire-performance requirements.
Across these sectors, cable selection directly affects maintenance cycles, system availability, and total operating cost.
Selecting the Right Industrial Cable
Choosing the correct cable involves more than matching voltage or conductor size. A practical evaluation should include:
-
Whether the application is static or dynamic
-
Mechanical stresses and movement cycles
-
Environmental exposure and temperature range
-
Applicable standards and certifications
-
Allowance for future system expansion
Working with suppliers who provide detailed technical data and testing documentation reduces long-term risk.
Standards, Compliance, and Risk Management
Industrial cables must comply with regional and international standards such as IEC, EN, UL, and RoHS. Compliance is not just a regulatory formality—it simplifies inspections, supports insurance requirements, and reduces liability.
Consistent adherence to recognized standards is a strong indicator of manufacturing discipline and product reliability.
Lifecycle Cost vs. Purchase Price
In industrial environments, the lowest upfront cost rarely equals the lowest total cost. Cable failures often result in production losses, labor expenses, and safety risks that far exceed the price difference between alternatives.
A well-specified industrial cable is designed to minimize maintenance, offer predictable service life, and support stable operation over many years.
Emerging Trends in Industrial Cable Technology
As industries become more automated and data-driven, cable technology continues to evolve. Current trends include:
-
Hybrid cables combining power and data
-
Increased use of fiber optics for noise immunity
-
Low-smoke, halogen-free materials for safety-critical spaces
-
Condition-monitoring features that support predictive maintenance
These developments reflect the growing role of cables as active contributors to system reliability rather than passive components.
Frequently Asked Questions
What qualifies a cable as “industrial”?
A cable designed to operate reliably under mechanical stress, environmental exposure, and strict safety requirements.
Are industrial cables suitable for outdoor use?
Yes, when specified with UV-resistant jackets and appropriate mechanical protection.
How long do industrial cables typically last?
Service life varies, but quality cables can last 10–30 years depending on application and environment.
Why is flexibility important in industrial applications?
In moving systems, flexibility prevents conductor fatigue and reduces failure risk.
Can industrial cables be customized?
Yes. Many applications require tailored conductor counts, shielding, or jacket materials.